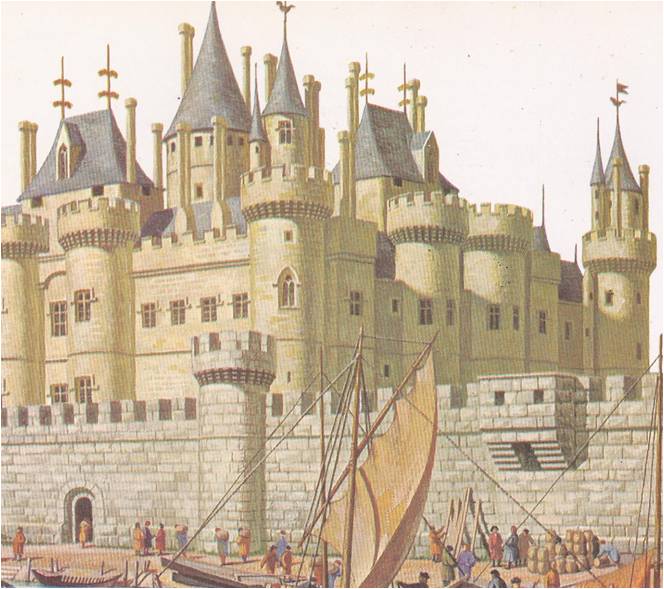
In 1600, the Duke Virginio Orsini‚ nephew of the Medici ruler of Florence, arrived in England. He came to spend the New Year’s holidays and to see for himself the woman who fascinated all Europe. She was Elizabeth, queen of England and she was already a legend. To aristocratic travelers, such as the Duke Orsini, she was the most important tourist sight in England. Years later, she would still be as fascinating as any woman in history, for in her time — the Elizabethan Age — her country flourished as never before and the Renaissance blossomed in England. As a …
Read More »Renaissance 1277 – 1603
The Renaissance in the North and Spain 1400 – 1598
Through the bustling market-towns of the Low Countries passed the traders, goods and gold of all Europe. Here the luxuries of Asia — spices‚ silks, jewels and perfumes — were exchanged for the practical products of the North — woolen cloth and utensils of iron and copper and wood. In shops and inns, wily Italian shippers and bankers bargained with the solemn, solid merchants from Germany and Flanders — and made the profits that built the Renaissance cities of Italy. In tall-spired cathedrals, in palaces, guildhalls and universities, wandering Italian artists discovered works of art and scholarship as great as …
Read More »The Italian Kings of France 1494 – 1590
In all Europe there was no greater admirer of Italy than Francis I, king of France. Francis practiced Italian manners in his court, built Italian palaces in his parks and kept Italian books in his library. He collected Italian paintings and the artists who painted them. Indeed, the king admired Italy so much that he wanted to conquer it all. Francis was not the first ruler to feel these strong Italian longings. In England, Spain and Germany, kings and princes were busily remodeling their courts, their castles and themselves in the Italian manner. Though the little states of Italy were …
Read More »Venice, City in the Sea 1350 – 1590
The houses of Venice are “like sea-birds half on sea and half on land,” said Cassiodorus. An officer of a king of the Goths, Cassiodorus saw Venice in 537. It was a little settlement of huts built on the mud-flats in an out-of-the-way lagoon. Its people were refugees‚ Italians who had been driven from their homes by a horde of barbaric invaders. They were safe in the lagoon, for no stranger could navigate the treacherous channels. For the sake of safety, they were content with comforts that were simple at best. “In this place,” Cassiodorus said, “rich and poor are …
Read More »Rome, the City of the Pope 1492-1564
In 1492, young Giovanni de’ Medici bade farewell to his father, Lorenzo the Magnificent and left Florence to take his place in Rome among the cardinals of the church. At sixteen, Giovanni was a nobleman in the court of the pope, a man of influence and power. That was fortunate, for when Giovanni was eighteen, his family’s power collapsed. The Florentines drove the Medici from their city and Giovanni, who had come home for a visit, narrowly escaped being stoned by the citizens who once had cheered him. As he crept out of the city, disguised as a poor friar, …
Read More »Gentlemen, Scholars and Princes 1400 – 1507
One day in the fifteenth century, the Turkish potentate of Babylonia decided to send gifts to the greatest ruler in Italy. He consulted his counselors and men who had traveled widely in Europe, asking them who best deserved this honour. They agreed that one Italian court outshone the rest and that his court must surely be the home of Italy’s mightiest sovereign. They did not name Milan, the home of the proud Sforza, nor Florence, the city of the clever Medici. The most magnificent court in Italy, they said, was at Ferrara, the capital of the dukes whose family name …
Read More »Milan, City of Splendour and War 1277-1515
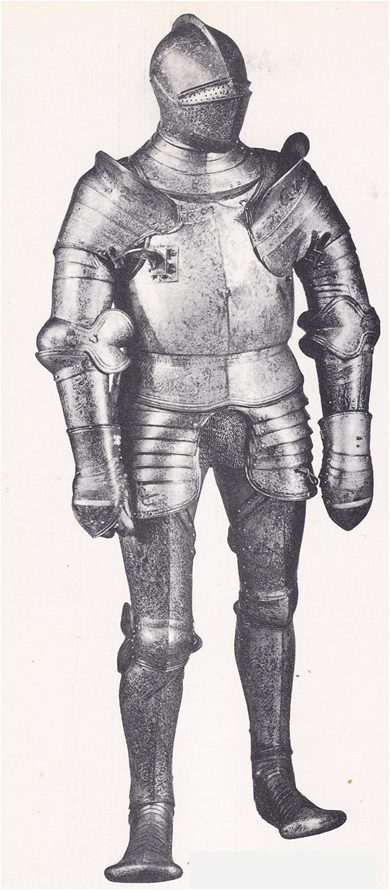
Milan’s most important business street had no displays of velvet cloaks, bright bolts of silk, or cloth-of-gold. It was a dusty, smoky street, made hot by the fires of forges and filled with the din of hammers shaping steel — the Street of the Armourers. Milan made the finest armour in the world. In the Middle Ages, the crusaders came there for chain mail and it was said that entire armies were outfitted in a few days. Later, the fashions of war changed. Knights wore heavy suits of jointed steel plates that covered them from head to toe and elegant …
Read More »Florence in the Golden Age 1469 -1498
Lorenzo de’ Medici was far from handsome. His skin was sallow, his eyes had a short-sighted squint and his nose was flat and wide. His voice was high and thin. Like every man in his family, he had the gout. Yet there was grandeur in everything Lorenzo did. He loved art and books, music and poetry and women. He delighted in sports, hunting and galloping across the brown Tuscan hills. He dealt with ambassadors like a prince, his palace was the gathering-place for the great men of Italy and his city won renown for both its scholars and its carnivals. …
Read More »Florence, First City of the Renaissance 1200-1480
March 25, 1436, was the Feast of the Annunciation and the city of Florence was decked out for a celebration. Banners flew everywhere, ribbons and garlands of flowers decorated the houses and draperies of cloth-of-gold were looped across the shop-fronts. The city bustled with excitement, for on this Annunciation Day the pope was to dedicate the Duomo, the wonderful new Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore, then the largest church in the world. At dawn, the people began to fill the streets. They crowded around the high wooden walk that led to the cathedral from the monastery where the pope …
Read More »The Sound of Bells and Trumpets in Europe 1300 – 1600
Bells and trumpets sounded across Europe in the time that men would call the Middle Ages. Knights in glistening armour rode forth to serve God and their kings; life was like a stately procession winding through a landscape marked by castles and cathedrals. Each man knew his place. He was a prince, a knight, a squire, a priest, a craftsman, or a serf. He wore the clothes that belonged to his rank — the armour and family emblems of a nobleman, the robes of a churchman, or the rough wool jerkin of a serf. He lived according to an age-old …
Read More »