One day in the fifteenth century, the Turkish potentate of Babylonia decided to send gifts to the greatest ruler in Italy. He consulted his counselors and men who had traveled widely in Europe, asking them who best deserved this honour. They agreed that one Italian court outshone the rest and that his court must surely be the home of Italy’s mightiest sovereign. They did not name Milan, the home of the proud Sforza, nor Florence, the city of the clever Medici. The most magnificent court in Italy, they said, was at Ferrara, the capital of the dukes whose family name …
Read More »Tag Archives: Babylonia
The Rise of the Assyrians 1600 B. C. – 539 B. C.
During the century after the Hittites had raided Babylon and rose to power in Turkey and Syria, Mesopotamia was a divided unproductive land. In the south, Babylonia fell under the rule of foreigners, first the Kassites from the northeast and then the Elamites from the southeast. Neither of these people seemed able to make any advances in civilization. Northern Mesopotamia came under the Mitanni kingdom, which at least introduced trained horses and chariots to the Near East. By the time the native Babylonians regained control and the Mitanni kingdom fell, another people was disturbing the land – the Assyrians. The …
Read More »Mesopotamia, Where Civilization Began 4000 B.C. – 1750 B.C.
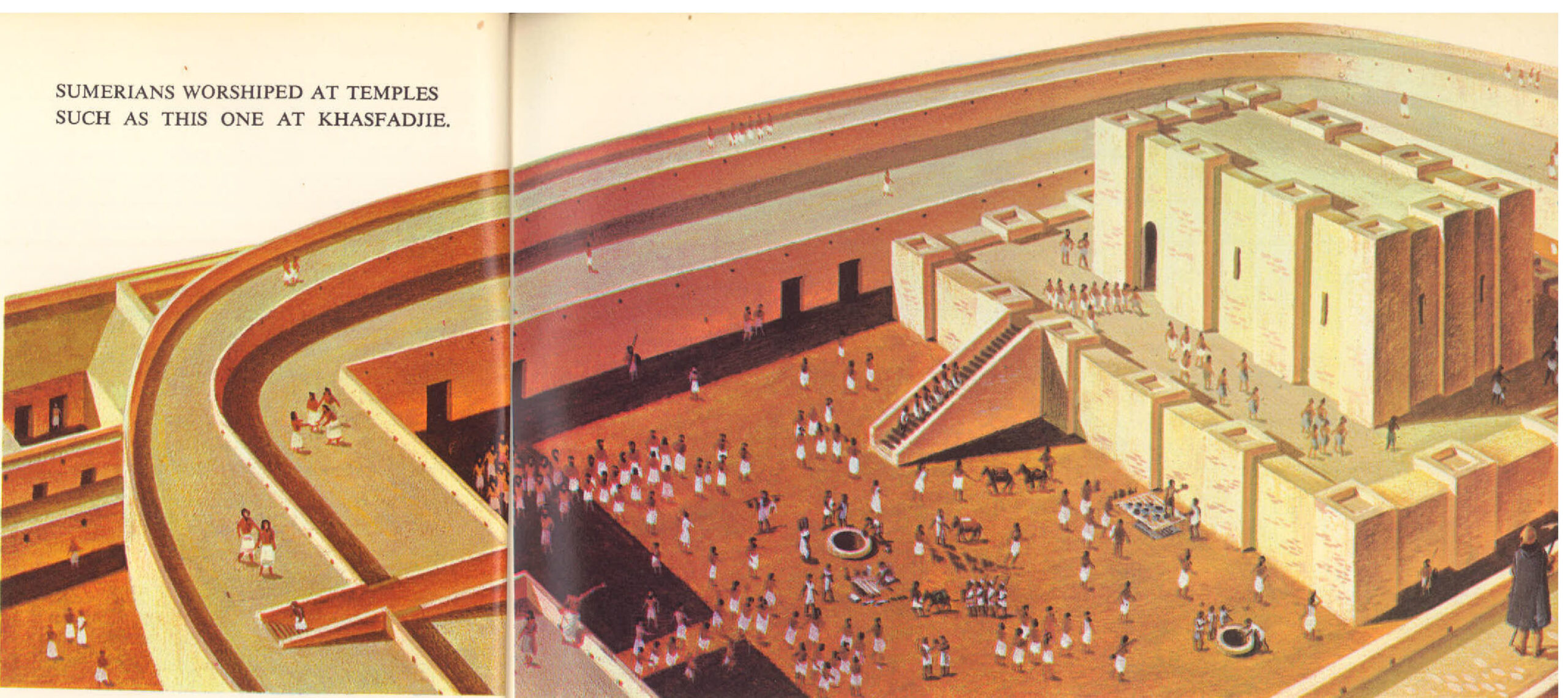
Mesopotamia is where civilization began. By 4000 B. C., many different groups of people were working out their lives in a variety of ways. In a great arc from the eastern coast of the Mediterranean, across the Turkish plains and through the highlands of Iraq and Iran, groups of peoples had settled and were farming, tending animals, making pottery and building towns, markets and forts. In the deserts, mountains and steppes, nomadic tribesmen lived by herding animals and by hunting and raiding. In Mesopotamia as these populations grew, they began to compete for land, food and supplies. One of the …
Read More »