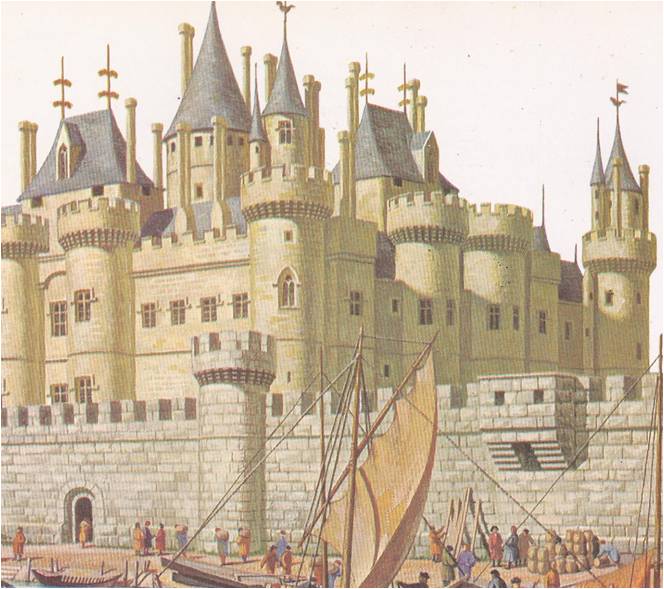
In all Europe there was no greater admirer of Italy than Francis I, king of France. Francis practiced Italian manners in his court, built Italian palaces in his parks and kept Italian books in his library. He collected Italian paintings and the artists who painted them. Indeed, the king admired Italy so much that he wanted to conquer it all. Francis was not the first ruler to feel these strong Italian longings. In England, Spain and Germany, kings and princes were busily remodeling their courts, their castles and themselves in the Italian manner. Though the little states of Italy were …
Read More »Tag Archives: Charles VIII
Milan, City of Splendour and War 1277-1515
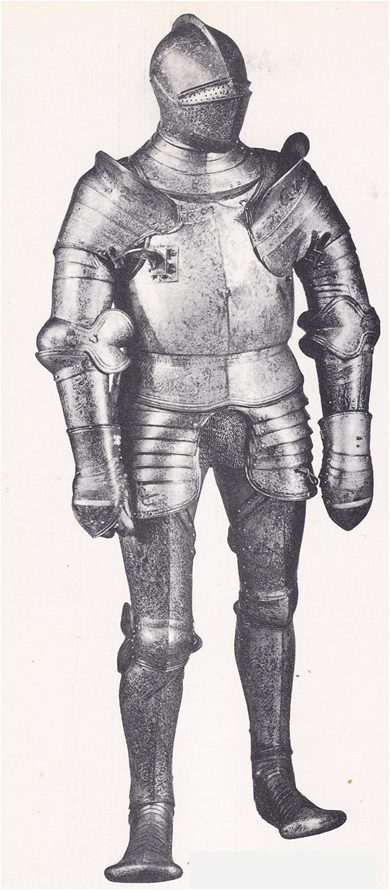
Milan’s most important business street had no displays of velvet cloaks, bright bolts of silk, or cloth-of-gold. It was a dusty, smoky street, made hot by the fires of forges and filled with the din of hammers shaping steel — the Street of the Armourers. Milan made the finest armour in the world. In the Middle Ages, the crusaders came there for chain mail and it was said that entire armies were outfitted in a few days. Later, the fashions of war changed. Knights wore heavy suits of jointed steel plates that covered them from head to toe and elegant …
Read More »The Hundred Years War 1326-1477
THE LONG STRUGGLE between France and England, known to history as the Hundred Years’ War, was not really a war — and it lasted more than a hundred years. Rather than a war, it was a series of separate battles, with periods of uneasy peace between and it lasted from 1338 to 1453. It was time of misery for both sides, but the French lost more men and saw much of their land devastated. By the end of the Hundred Years’ War, important changes had taken place in both countries. In France, the years of conflict weakened the power of …
Read More »