On May 11, 1860 an almost incredible military campaign began with the landing of Guiseppe Garibaldi on the western tip of Sicily. Garibaldi was a handsome, dashing, reckless warrior patriot. With him were a thousand devoted followers, clad in red shirts. Maybe red shirts were easier to shoot at than green or gray, but for every bullet, they attracted a recruit from the ranks of the enemy. The island of Sicily was one of the two parts of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The other “Sicily” was the southern third of the peninsula of Italy. The capital of the …
Read More »Tag Archives: Naples
The Rise of Napoleon Bonaparte 1796-1802
In March of 1796, a new commander named Napoleon Bonaparte was placed in charge of the French army on the Italian front. The soldiers and officers were amazed when they first saw him. He was short, thin, pale, only twenty-seven years old and spoke French with an Italian accent. Napoleon was not an unknown. He had first come to public attention as the young artillery officer who drove the British fleet from the harbour at Toulon. Later, as a brigadier general, he had successfully defended the Convention from an uprising in Paris. What most people did not know was that …
Read More »The Monk from Wittenberg 1505-1546
ON A SULTRY JULY DAY IN 1505, a young law student, Martin Luther, was walking along a country road in Germany when a summer storm blew up. The air grew heavy and black clouds filled the sky. Before Luther could take shelter, thunder began to crash. A bolt of lightning struck the road almost at his feet. Thrown to the ground, he lay shaking, not certain whether he was alive or dead. “Help me, Saint Anne,” he cried, “help me and I will become a monk.” After a moment, Luther’s trembling stopped. He stood up, found that he was not …
Read More »The Renaissance in the North and Spain 1400 – 1598
Through the bustling market-towns of the Low Countries passed the traders, goods and gold of all Europe. Here the luxuries of Asia — spices‚ silks, jewels and perfumes — were exchanged for the practical products of the North — woolen cloth and utensils of iron and copper and wood. In shops and inns, wily Italian shippers and bankers bargained with the solemn, solid merchants from Germany and Flanders — and made the profits that built the Renaissance cities of Italy. In tall-spired cathedrals, in palaces, guildhalls and universities, wandering Italian artists discovered works of art and scholarship as great as …
Read More »Rome, the City of the Pope 1492-1564
In 1492, young Giovanni de’ Medici bade farewell to his father, Lorenzo the Magnificent and left Florence to take his place in Rome among the cardinals of the church. At sixteen, Giovanni was a nobleman in the court of the pope, a man of influence and power. That was fortunate, for when Giovanni was eighteen, his family’s power collapsed. The Florentines drove the Medici from their city and Giovanni, who had come home for a visit, narrowly escaped being stoned by the citizens who once had cheered him. As he crept out of the city, disguised as a poor friar, …
Read More »Milan, City of Splendour and War 1277-1515
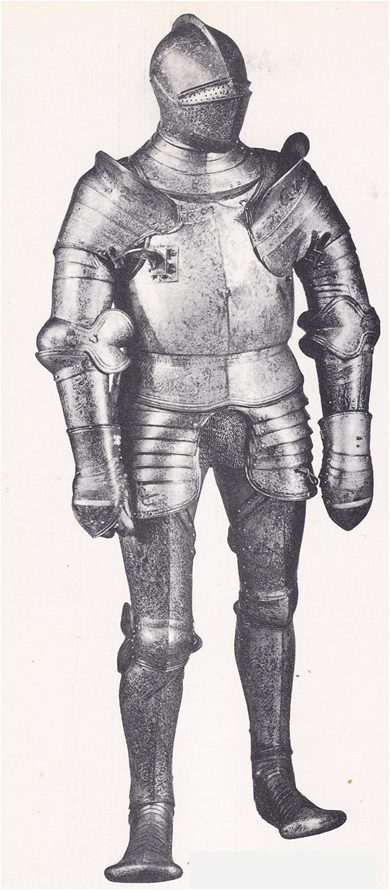
Milan’s most important business street had no displays of velvet cloaks, bright bolts of silk, or cloth-of-gold. It was a dusty, smoky street, made hot by the fires of forges and filled with the din of hammers shaping steel — the Street of the Armourers. Milan made the finest armour in the world. In the Middle Ages, the crusaders came there for chain mail and it was said that entire armies were outfitted in a few days. Later, the fashions of war changed. Knights wore heavy suits of jointed steel plates that covered them from head to toe and elegant …
Read More »Florence in the Golden Age 1469 -1498
Lorenzo de’ Medici was far from handsome. His skin was sallow, his eyes had a short-sighted squint and his nose was flat and wide. His voice was high and thin. Like every man in his family, he had the gout. Yet there was grandeur in everything Lorenzo did. He loved art and books, music and poetry and women. He delighted in sports, hunting and galloping across the brown Tuscan hills. He dealt with ambassadors like a prince, his palace was the gathering-place for the great men of Italy and his city won renown for both its scholars and its carnivals. …
Read More »Florence, First City of the Renaissance 1200-1480
March 25, 1436, was the Feast of the Annunciation and the city of Florence was decked out for a celebration. Banners flew everywhere, ribbons and garlands of flowers decorated the houses and draperies of cloth-of-gold were looped across the shop-fronts. The city bustled with excitement, for on this Annunciation Day the pope was to dedicate the Duomo, the wonderful new Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore, then the largest church in the world. At dawn, the people began to fill the streets. They crowded around the high wooden walk that led to the cathedral from the monastery where the pope …
Read More »