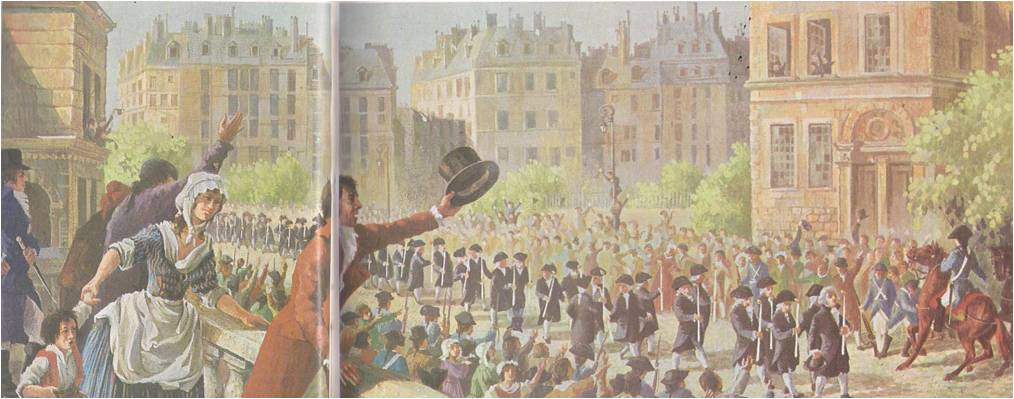The year is 1789; the place, Versailles, France. Several hundred delegates representing the people of France sit sullenly in the palace hall. When an officer of the King orders them to leave the hall and return to their proper meeting place, one delegate rises to his full height and thunders, “Tell your master that we are here by the will of the people, and that only bayonets can drive us forth” A meeting of representatives of the French people? Defiance to the commands of the powerful king of France? In view of what you have read earlier about royal authority …
Read More »Tag Archives: Versailles
France Becomes the Leading Country of Europe
From early morning until midnight every great French noble and those who hoped to be great, worked at doing and saying what would please the King in his palace at Versailles. From all over France came these noblemen, for the only road to success was by way of the Grand Monarch’s favour. In 1670 a French bishop described the tremendous power of the King in these words: “Behold an immense people united in a single person; . . you see the image of God in the King, and you have the idea of royal majesty . . . borrowed from …
Read More »Another Napoleon 1848-1906
IN DECEMBER of 1848, the French elected Louis-Napoleon Bonaparte as president of the Second French Republic. What he stood for was not very clear, but to most Frenchmen that did not seem important. He was the nephew of the great Napoleon and the very sound of his name stirred them like a battle-cry. Since the defeat of the first Napoleon in 1815, there had been little in French politics to capture the imagination. As the years passed, the French looked back on the Napoleonic era as the time of their greatest glory. The writer Victor Hugo wrote poems about Napoleon. …
Read More »“The King to Paris!” 1789
In the towns and cities of the provinces, the news of the fall of the Bastille led to wild celebrations and a series of revolts against local governments. These governments had long been unpopular, since most of them were controlled by nobles and others who had bought their government positions from the king. The town people set up new governments, similar to the one in Paris and organized local units of the National Guard. The revolution spread to the countryside as well. There the peasant uprising had started even before the fall of the Bastille. The peasants made up at …
Read More »The Fall of the Bastille 1789
On Sunday, July 12, 1789, the people of Paris learned that Necker, the popular minister, had suddenly been dismissed by the king. They could only guess at the king’s reasons for wanting Necker out of the way. It seemed clear enough that Necker’s dismissal had something to do with the recent arrival of Swiss and German troops in the Paris area. It was said that more troops were arriving every day. Why? People were almost afraid to guess at the answer. The news of Necker spread quickly and angry crowds gathered in the streets. A young man named Desmoulins leaped …
Read More »The Voice of the People 1789
The sun had broken through the clouds after a night of spring showers. Dripping leaves sparkled in the golden light, which flooded the gaily decorated streets of Versailles and the broad terraces of the king’s royal palace. It was May 4, 1789, the day of the opening ceremony of the recently elected Estates General. The streets were crowded with visitors, most of them from Paris, only a few miles away. They had come to see the grand procession of the Estates General and were in a holiday mood. The shops were closed. Local citizens watched from windows, crowded balconies and …
Read More »The Sun King 1642 – 1715
ALL HIS LIFE Cardinal Richelieu had been a sick man, but by the spring of 1642 he was dying. He carefully made his will, leaving to the king his elegant town house, eight sets of tapestries‚ and three beds. On December 2, he received the last sacraments of his church. “Does your Eminence pardon your enemies?” asked the priest and Richelieu answered, “I have no enemies but those of the State.” When Louis XIII learned that Richelieu had died, he said, “A great statesman is dead.” To take Richelieu’s place, Louis chose Jules Cardinal Mazarin, Richelieu’s own choice for his …
Read More »