At Olympia every four years Olympic games were held in which any Greek was entitled to take part. It is not known when the first Olympic games were held, but they were said to have been revived in the year 776 B.C. and the Greeks used that year from which to reckon dates. The period of four years between each celebration of the olympic games was called an Olympiad. When therefore a Greek writer says something happened in the year of the . . . Olympiad we can calculate the year according to our system and put it down as . . . B.C. From now onwards Greek history becomes more exact.
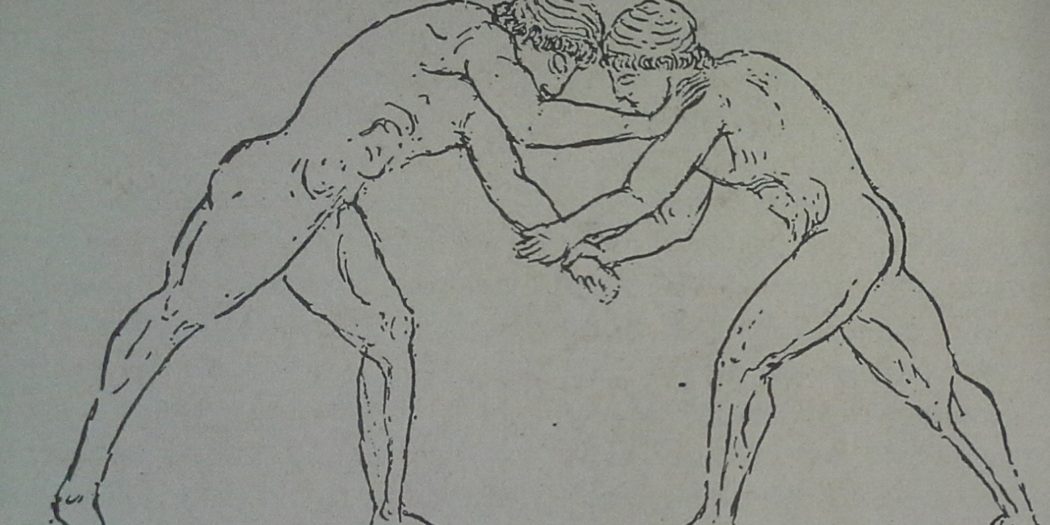
Like Delphi, Olympia became a place where men from any part of the Greek world might meet. For a month every four years the incessant quarrels of the city-states were stopped and during five days of this truce period the olympic games were held. There was running, long jump, boxing. wrestling, throwing the discus or javelin, chariot racing and horse racing (all individual events — no team games) and no Marathon. The only prize at Olympia was a crown of wild olive, but when victorious, competitors reached home they were given a variety of honours and rewards. At Athens they received a large sum of money and the right to free dinners for life (cf. p. 60). At Sparta they were assigned the post of honour in battle.