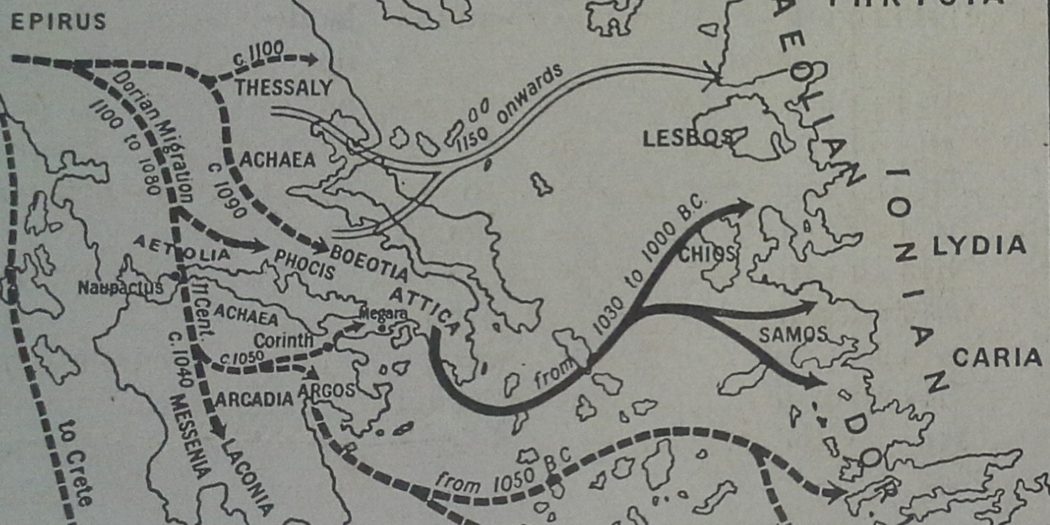
The “Dark Age” of Greece (c. 1100 – 800) was a time of migration and settlement. Whole peoples were in migration mode. People on the move do not have time to write records for us to read later nor do they build palaces which we can dig up. So there is no continuous history of this period, though during it Homer (c. 900) and Hesiod (c. 800) wrote their poems. (Hesiod’s contained two very different ingredients — stories of the gods and practical advice about country life.)
The Achaeans were overcome by invaders from the north called Dorians, who occupied the Peloponnese. Some of them also occupied part of the coast of Asia Minor and Crete. The Dorians did not invade the peninsula on which Athens stood, but Achaeans and kindred peoples called Ionians, who had been forced out of other parts of Greece, took refuge there. In time some of these migrated to Asia Minor. The coastal area which they occupied was called Ionia.
The distinction between Dorian and non-Dorian parts of Greece gradually ceased to be important. The point to remember about the Dorian invasion is that it left Greeks settled in Ionia as well as on the Aegean islands and the mainland. They were destined, however, to go further afield than that.