After a battle there is a great deal of clearing up to be done. A small part of the Athenian force had been left behind to do this. The general in command was Aristides. “The Just”. There was no fear of his taking any of the rich Persian spoil for himself. He had gained a reputation for scrupulous honesty, for putting country before self and for modest behaviour. These qualities were rare. Perhaps as he returned to the Athenians after completing his task at Marathon, he felt that he had a good chance of occupying a powerful position such as had been held by Cleisthenes, whom he had known and admired.
Far from it. A few years later Aristides was ostracised. On the day when the votes were cast it is said that an illiterate citizen, who did not even know Aristides by sight, came up to him and asked for help in marking the piece of broken pottery which served as a voting paper. The citizen wanted “Aristides” written on his. The owner of the name was a little surprised and asked the citizen whether Aristides had injured him in any way. “Oh no,” was the answer. “I haven’t even met him. But I’m tired of hearing him called ‘The Just’.” Aristides did not argue but wrote his name on the piece of pottery. If he had had less high principles and more sense of humour he would have written the name of his rival – Themistocles.
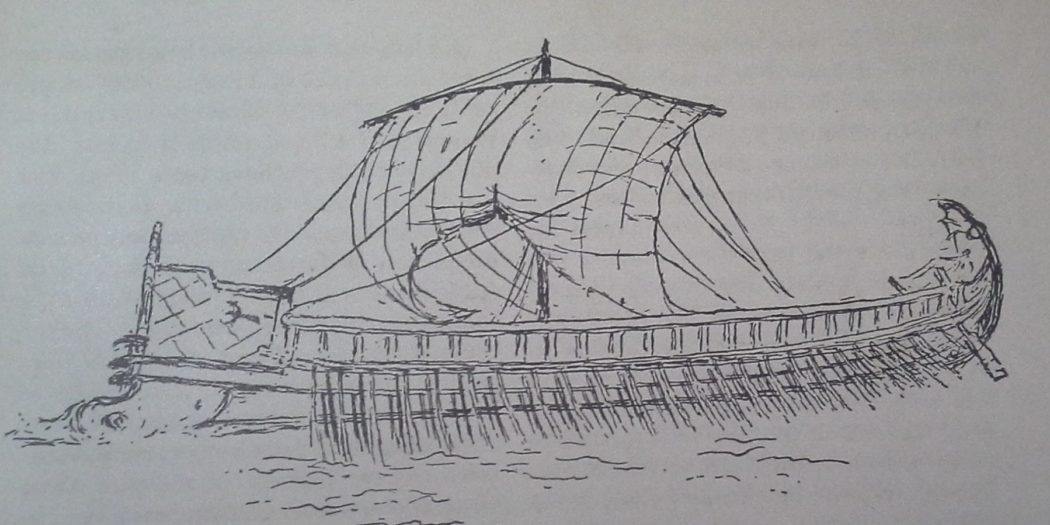
Themistocles was pushy and boastful. In the company of artistic people he said, with slimy mock-modesty: “I’m sorry I can’t play any musical instrument. All I can do is to make a small city into a great one.” When a visitor from one of the Aegean islands belittled the fame Themistocles had won and said it belonged not to him but to Athenians and Athens, Themistocles quickly retorted: “True, I would not have been famous had I lived on your island, but neither would you have been, if you had lived in Athens with Athenians.” He had a spoilt young son, whom he used to call the most powerful person in Greece, explaining: “The Athenians command the rest of Greece, I command the Athenians, your Mother commands me and you command your mother.” Yet he was popular. He knew how to flatter his audience, whereas Aristides probably did not bother. He was also extremely far-sighted. In the year when his rival was ostracised there was a surplus from the state-owned silver mines at Laurium (see map) which would normally have been distributed among the citizens. Themistocles persuaded them to use it instead to build two hundred triremes (opposite). These warships saved Greece from Persia’s second attack and laid the foundations of a naval supremacy which was to make Athens and Athenians rich and famous.
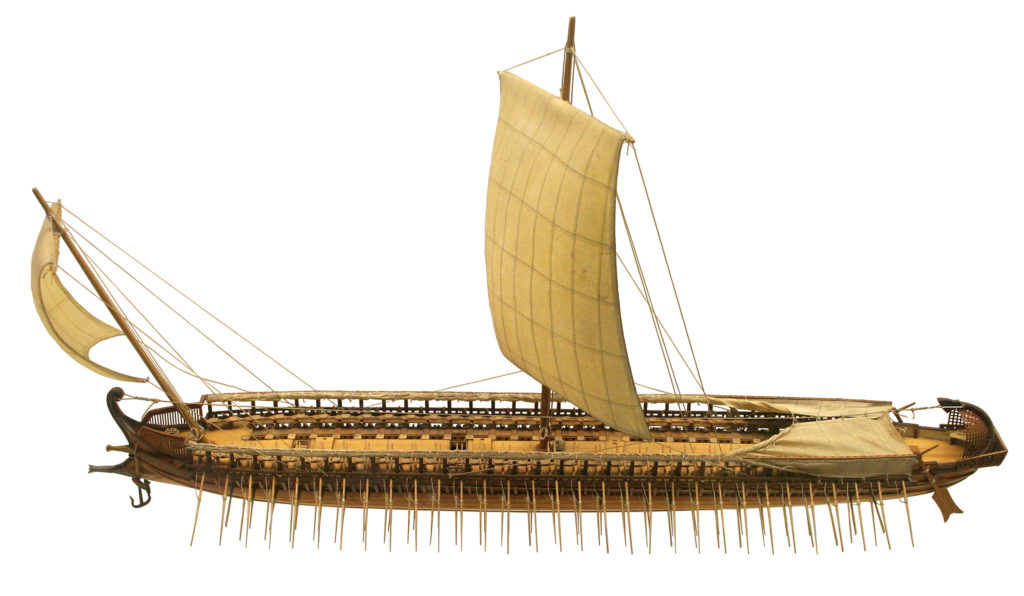

Steering was done by two oars in the stern. A mainsail was carried for running before the wind. A speed of 7 knots could be kept up for some time and Journeys of 50 miles a day were not unusual. The commander, a ‘trierarch’, had to be rich, since he paid the maintenance and repair of the ship.